
How to close the age gap in clinical cancer research?
From geriatric assessment to artificial intelligence, an ESMO/SIOG paper highlights effective strategies to improve the representation of older patients in clinical trials

Research unlocks insights into lung cancer evolution from electronic medical records
A domain-specific natural language processing (NPL) pipeline showed strong performance in extracting clinically meaningful information from diverse clinical documents of patients with non-small cell lung cancer

RAS inhibition: a game changer in pancreatic cancer?
Preclinical findings show antitumour activity of triple KRAS inhibition in mouse models, but it will take years of rigorous research to assess its clinical efficacy in oncology patients

Structured exercise enters ESMO guidelines for colon cancer as recommended treatment
The update reflects survival benefits of post-diagnosis exercise in stage II–III colon cancer as recently reported in the CHALLENGE study
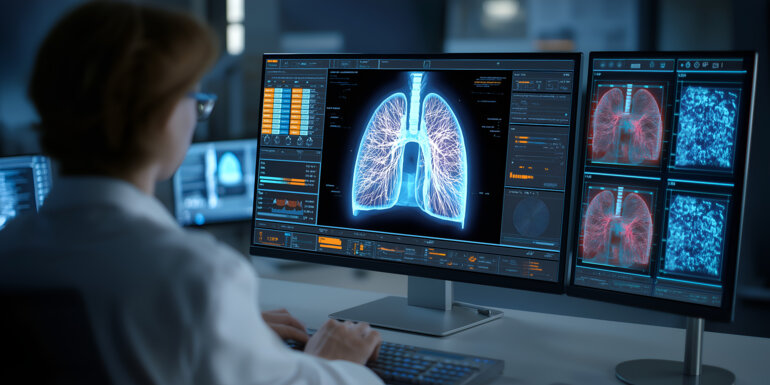
Study supports radiomics in predicting immunotherapy effectiveness in advanced NSCLC
In a real-world study, multimodal artificial intelligence models outperform PD-L1 across key endpoints

Next-generation KRAS G12C inhibitor shows promising activity in advanced colorectal cancer
Manageable safety and encouraging antitumour responses were presented with MK-1084 monotherapy and combination regimens

Study provides prospective validation of an alternative biopsy technique
Data shows that index lesion-focused ipsilateral systematic biopsy is not inferior to standard systematic biopsy

AI model boosts survival prediction accuracy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer
A study compared the performance of different models using routinely collected clinicopathological data from women with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer

Next-generation PRAME-directed TCR T-cell therapy shows early activity in solid tumours
Tumour reduction was observed with IMA203CD8 across different PRAME-expressing cancers in a phase I trial

Retifanlimab prolongs overall survival in advanced squamous cell anal cancer
Benefits were seen across most predefined subgroups investigated in the practice-changing POD1UM-303/InterAACT-2 study
