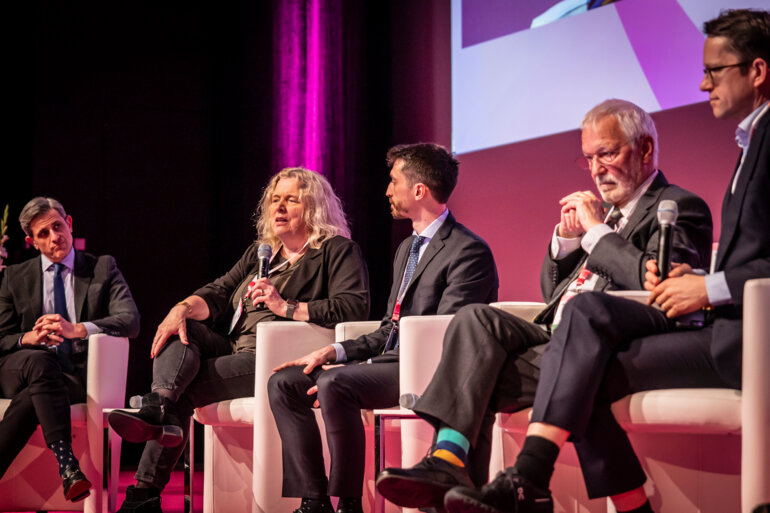

Tailored use of chemotherapy may benefit some early-stage ER+/HER2– breast cancers
Results from two studies suggest that withholding chemotherapy for some patients may not impact efficacy, but an understanding of clinical and biological features is paramount
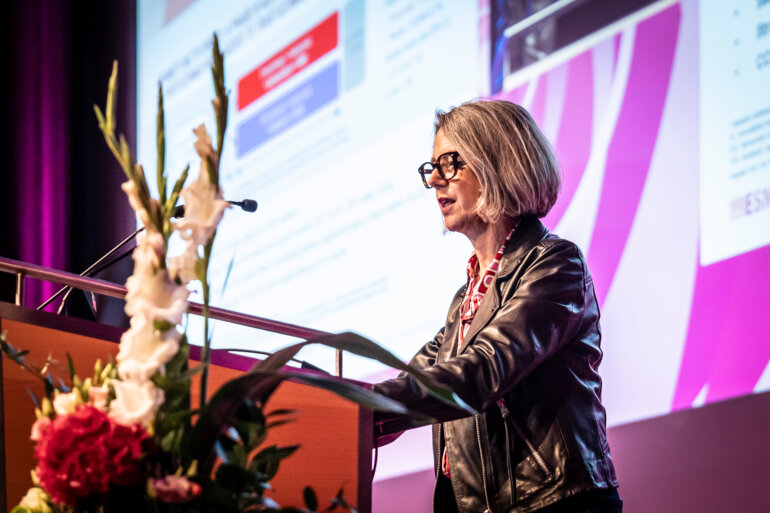

Adding adjuvant pertuzumab demonstrates prolonged survival benefit after 10+ years in HER2+ breast cancer
Final long-term overall survival data from APHINITY confirm the efficacy of dual HER2 blockade in patients with node-positive disease

Study findings refine the use of ctDNA to track resistance to endocrine therapy in advanced breast cancer
A timing window for testing ESR1 mutations in the blood was identified
Will AI reshape breast cancer screening?
While AI tools have shown promise in reducing false positives and aiding radiologists, large prospective trials are now exploring how technology should be integrated in screening programmes

Caring for underserved cancer patient populations
ESMO continues its commitment to gender-diverse and sex-specific oncology to address the growing need to close knowledge gaps among oncologists

Research offers novel insights to refine first-line treatment in GEP-NETs
Data from new clinical trials reported positive results of radioligand therapy over everolimus and sunitinib, and explore the combination of everolimus and somatostatin analogues

AI applications in oncology go beyond clinical practice
While many models and tools are designed to support clinical decision-making, AI is already serving cancer research for background tasks, with some potential to educate patients too

An ESMO roadmap for implementing molecular tumour boards
Newly released recommendations address key areas to facilitate the integration of precision oncology in clinical practice

Perioperative durvalumab led to encouraging survival data in resectable NSCLC
An improvement was observed when immunotherapy was added to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, but further data are needed to confirm the survival benefit

Overall survival benefit achieved with amivantamab plus lazertinib in advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC
Final results from the MARIPOSA trial provide further supporting evidence to the first-line treatment combination
