New data from the ALINA study confirm lack of influence of EML4-ALK variant on outcome in this patient population
At the ESMO Congress 2024 (Barcelona, 13–17 September), results of biomarker analysis of the phase III ALINA trial revealed that the disease-free survival (DFS) benefit of alectinib over chemotherapy in resected ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) occurred regardless of the type of EML4-ALK fusion variant (Abstract 1206MO). The most common variants in the 81% of patients with EML4-ALK fusions were V1 (37%) and V3 (33%).
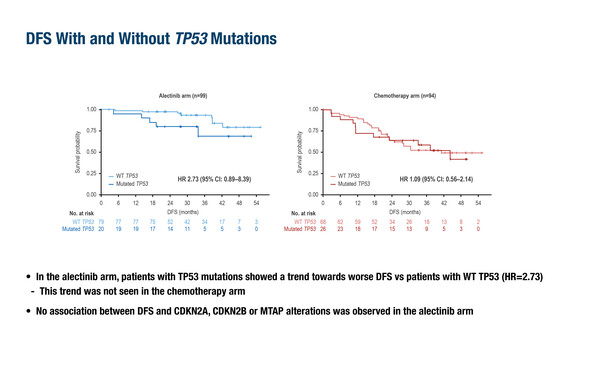
Among the 193 patients in the trial’s biomarker-evaluable population, there were 13 DFS events with alectinib and 41 with chemotherapy. There was a trend for improved DFS with wild-type TP53 compared with mutated TP53 in patients receiving alectinib but not in those receiving chemotherapy. Notably, no correlation was observed between DFS and CDKN2A, CDKN2B or MTAP alterations with alectinib treatment. Additionally, no ALK on-target resistance mechanisms were observed at recurrence.
This exploratory analysis of the ALINA trial (N Engl J Med. 2024;390:1265–1276) included patients receiving alectinib who had baseline tissue samples and matched samples at recurrence. The most commonly altered genes were CDKN2A, CDKN2B, TP53 and MTAP, with CDKN2A, CDKN2B and MTAP alterations commonly co-occurring in single tumours.
The findings from the ALINA biomarker analysis broadly echo those observed in the phase III ALEX trial of alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated advanced ALK-positive NSCLC (J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14:1233–1243). However, TP53 mutations were less prevalent in ALINA’s early-stage NSCLC population (24%) than in ALEX’s metastatic NSCLC patients (41%).
Programme details
Solomon BJ, et al. ALINA: Exploratory biomarker analyses in patients (pts) with resected ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with adjuvant alectinib vs chemotherapy (chemo). ESMO Congress 2024, Abstract 1206MO
Mini Oral Session 2 – Non-metastatic NSCLC, 16.09.2024, h. 14:45 – 15:45, Sevilla Auditorium – Hall 2