The optimal chemotherapy regimen in this setting is not well-defined
The most common first-line treatment for patients with advanced neuroendocrine carcinomas (NECs) is platinum–etoposide chemotherapy; however, on disease progression, second-line treatment is less well-defined.
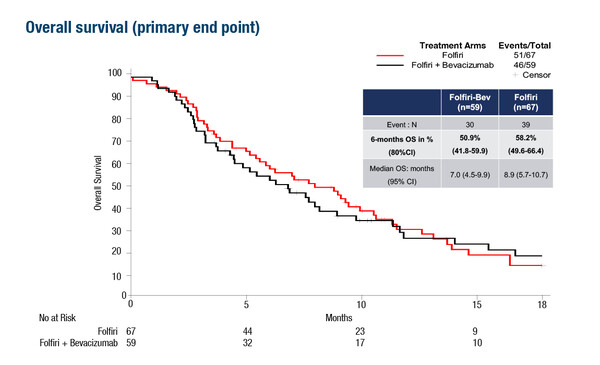
At ESMO Congress 2022, promising results were reported from the phase II PRODIGE 41-BEVANEC trial, which evaluated second-line FOLFIRI (folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil [5-FU] and irinotecan) plus bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI alone in 133 patients with advanced gastroenteropancreatic (GEP) NECs who had progressed on platinum–etoposide chemotherapy (LBA46). The primary objective was to demonstrate a 6-month overall survival (OS) rate of ≥50% in the experimental arm (efficacy was defined as ≥26/52 patients alive at 6 months; power 85%; one-sided alpha risk 10%). The primary objective was met, with 30/59 patients alive in the FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab arm and 5 patients with follow-up of less than 6 months, corresponding to a 6-month survival rate of 50.9% (80% CI 41.8–59.9). Median OS was 7.0 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 4.5–9.9) with FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab versus 8.9 months (95% CI 5.7–10.7) with FOLFIRI, and median progression-free survival (PFS) was 3.7 months (95% CI 1.9–5.6) and 3.5 months (95% CI 1.9–5.1), respectively. Objective response rates (25.5% versus 18.3%) and biochemical response rates were higher, and duration of response was longer, with FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab than FOLFIRI. One treatment-related death occurred in the combination arm.
Commenting on these data, Dr Nicola Fazio from the European Institute of Oncology, Milan, Italy says, “While these results are promising, they seem to reinforce the role of FOLFIRI rather than indicate the introduction of bevacizumab in the second-line treatment of NECs after platinum–etoposide failure. The potential benefits of the combination of liposomal irinotecan (nal-IRI), 5-FU and folinic acid are also supported by data from the NET-02 study, which met its primary endpoint earlier this year.” In this phase II study in patients with progressive extra-pulmonary NECs, a 6-month PFS rate of 32.1% was achieved with the combination of nal-IRI, 5-FU and folinic acid as second-line therapy. In contrast, patients randomised to single agent docetaxel achieved a 6-month PFS of only 14.8% (J Clin Oncol. 2022;16(Suppl):4005).
At ESMO Congress 2022, results were also reported from the phase III SEQTOR (GETNE 1206) trial, which compared the efficacy and safety of everolimus – a protein kinase inhibitor – followed by chemotherapy (streptozotocin and 5-FU) on progression (arm A) with the reverse sequence (arm B) in 141 patients with advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (panNETs) (LBA45). In this study, no difference was observed in PFS with the first assigned treatment (PFS1), with median PFS1 of 21.5 months (95% CI 16.9–31.3) and 23.6 months (95% CI 13.4–30.4) in arms A and B, respectively (p=0.351). Objective response rates were 11% in arm A and 30% in arm B (p=0.014), and clinical benefit rates were 92% and 80%, respectively (p=0.07). Stable disease was the most common outcome.
Regarding these results, Fazio says, “Unfortunately this study did not provide any additional information on the best therapy sequence for panNET with regard to PFS, but did suggest that using chemotherapy as the first treatment may be better than everolimus in terms of tumour response rate. Future subgroup analyses from this study will be highly valuable in order to identify and validate potential predictive factors that may determine the patients who will derive the most benefit from everolimus or chemotherapy treatment.” For patients with advanced panNETs, the benefits of chemotherapy have also been shown in the phase II E2211 trial, with preliminary data recently presented at ASCO 2022. This phase II study met its primary endpoint, with a median PFS of 14.4 months reported for patients treated with temozolomide monotherapy (a less toxic and oral novel alkylating agent) compared with 22.7 months for patients treated with temozolomide plus capecitabine (hazard ratio 0.58; p=0.022) (J Clin Oncol. 2022;16(Suppl):4004).
Fazio concludes: “First of all the co-authors of the BEVANEC and SEQTOR studies should be congratulated for their efforts, with the long recruitment periods highlighting the difficulty in conducting such trials. The results from BEVANEC for colorectal NECs suggest that an adenocarcinoma-like approach should be considered, with FOLFIRI–bevacizumab or even FOLFOXIRI–bevacizumab investigated as first-line treatment. For SEQTOR, the 1-year PFS data are not particularly informative for clinical practice, although they were impressively long in both arms. Sub-analyses to identify potential predictive factors for treatment response could be more useful.”
Abstracts presented:
Walter TA, et al. Bevacizumab (B) plus FOLFIRI after failure of platinum-etoposide in patients (pts) with advanced neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC): the PRODIGE 41-BEVANEC randomized phase II study. ESMO Congress 2022, LBA46
Mini Oral Session – NETs and endocrine tumours, 12.09.2022, h. 08:30 – 10:00, Quimper Auditorium
Salazar R, et al. Randomized open label phase III study comparing the efficacy and safety of everolimus followed by chemotherapy (CT) with streptozotocin (STZ)-5FU upon progression or the reverse sequence, in advanced progressive panNETs: the SEQTOR study (GETNE 1206). ESMO Congress 2022, LBA45
Proffered Paper Session – NETs and endocrine tumours, 12.09.2022, h. 16:30 – 18:00, Orléans Auditorium