Addition of abiraterone acetate plus prednisone shows clear survival improvements in castration-sensitive prostate cancer
Two trials presented in today’s Presidential Symposium 2 highlight the benefits of treatment intensification with androgen receptor signalling inhibitors in patients with hormone/castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC).
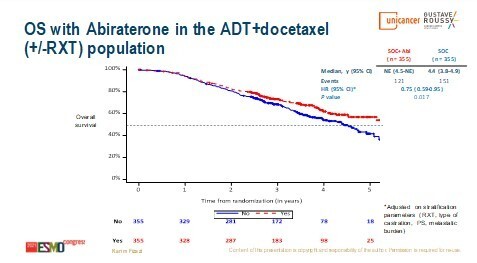
The PEACE-1 phase III trial investigated adding abiraterone acetate–prednisone (AAP) ± local radiotherapy to standard of care (androgen deprivation therapy [ADT] ± docetaxel; the addition of docetaxel became the new standard of care after the start of the study) in 1173 patients with de novo metastatic CSPC (LBA5_PR). Median overall survival (OS) was improved with the addition of AAP, both in the overall population (5.7 years versus 4.7 years; hazard ratio [HR] 0.82; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.69–0.98; p=0.030) and in the subpopulation of patients receiving ADT plus docetaxel (not reached versus 4.4 years; HR 0.75; 95% CI 0.59–0.95; p=0.017). Among patients who developed castration-resistant disease in the ADT plus docetaxel standard-of-care control arm, 84% then received at least one life-prolonging therapy and 81% received next-generation hormonal therapy, compared with 74% and 46%, respectively, of patients in the ADT plus docetaxel plus AAP arm. Toxicity was as expected, with no apparent synergistic adverse events from the combination.
“These results will change the standard of care,” says Dr Maria De Santis from Charité Universitätsmedizin, Berlin, Germany and the Medical University of Vienna, Austria. “In an earlier analysis of PEACE-1, the addition of AAP to ADT plus docetaxel significantly prolonged radiographic progression-free survival (J Clin Oncol 2021;39(15 Suppl):5000) but here, an obvious improvement in OS has been demonstrated, which extends the advances recently made in metastatic CSPC.” Reflecting on previous findings in this setting, De Santis adds, “In patients with metastatic CSPC, we already knew that early treatment intensification improved survival significantly, but the question was if doublets or triplet therapy should be used. This has now been answered in the PEACE-1 study.”
This is a completely new patient (sub)group that has not been included in other published trials.
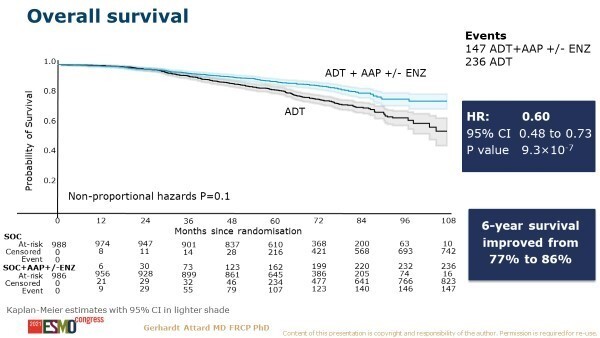
Similarly encouraging results were also presented in the non-metastatic CSPC setting. A primary combined analysis from two comparisons in the STAMPEDE platform protocol assessed AAP ± enzalutamide added to ADT compared with ADT alone (LBA4_PR). There was significant improvement in the primary endpoint of metastatic-free survival (MFS) with 2 years of AAP-based therapy than with ADT alone (108 events versus 306 events, respectively; HR 0.53, 95% CI 0.44–0.64, p<0.0001). OS was also significantly improved with the combination regimen (147 deaths versus 236 deaths, respectively; HR 0.60, 95% CI 0.48–0.73; p<0.0001) (Figure). Adding enzalutamide to AAP increased toxicity, but this was described by the researchers as having ‘no discernible effect on efficacy’.
“For patients with high-risk, locally advanced disease – the so-called M0 CSPC setting – we have been eagerly awaiting OS data for several years,” says De Santis. “Until now it was unclear if the major failure-free survival improvements would translate into an OS benefit. This is a completely new patient (sub)group that has not been included in other published trials. With the clinically relevant improvements in survival seen in STAMPEDE, I expect this kind of treatment intensification to be implemented as a standard of care.”
With these findings, current practice is likely to change relatively quickly in both metastatic and high-risk locally advanced CSPC since the agents investigated are already approved and available in clinical practice, although these studies suggest a different, more effective way to use them. “AAP has become generic and is currently much cheaper than other androgen receptor signalling inhibitors. Hopefully, reimbursement will not be an issue given the significant OS improvement and the benefits for our patients,” concludes De Santis, who is optimistic about the safety data presented today. “The huge benefits of these treatments and combinations clearly outweigh the risks of well-known agents. The overwhelmingly positive results are reassuring and will help to convince patients and physicians to intensify treatment early on.”
Fizazi K et al. A phase III trial with a 2x2 factorial design in men with de novo metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer: Overall survival with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in PEACE-1. ESMO Congress 2021, Abstract LBA5_PR
Presidential symposium 2, 19.9.2021, h. 15:05 – 16:37, Channel 1
Attard G et al. Abiraterone acetate plus prednisolone (AAP) with or without enzalutamide (ENZ) added to androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) compared to ADT alone for men with high-risk non-metastatic (M0) prostate cancer (PCa): Combined analysis from two comparisons in the STAMPEDE platform protocol. ESMO Congress 2021, Abstract LBA4_PR
Presidential symposium 2, 19.9.2021, h. 15:05 – 16:37, Channel 1