A study reports no significant survival benefits with the concurrent treatment with durvalumab in patients with unresectable stage III NSCLC
Starting immunotherapy concurrently with chemoradiotherapy (CRT), followed by consolidation immunotherapy, in patients with unresectable, stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) does not improve outcomes compared to chemoradiotherapy alone, as reported by the final results of the PACIFIC-2 trial presented at the European Lung Cancer Congress 2024 (Prague, Czech republic, 20–23 March) (LBA1).
In the phase III, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, global study, 328 treatment- naïve patients with stage III NSCLC were randomised (2:1) to either receive CRT plus durvalumab or placebo intravenously every 4 weeks, and a consolidation therapy with durvalumab or placebo until disease progression.
CRT followed by 12 months of consolidation durvalumab is considered the standard of care for patients with unresectable, stage III NSCLC after it demonstrated a sustained 5-year overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) improvement in the PACIFIC trial (N Engl J Med 2017; 377:1919-1929). However, up to one third of patients are not eligible for the consolidation therapy due to disease progression during or immediately after concurrent CRT, radiation pneumonitis, or other adverse events.
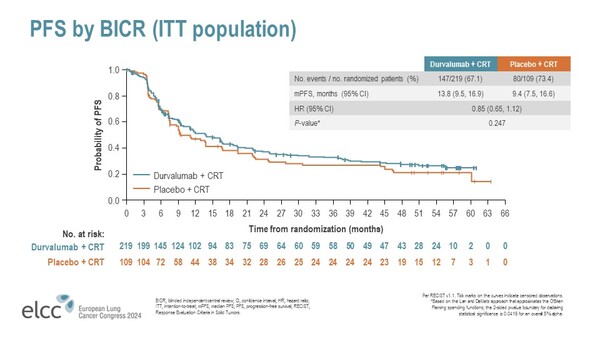
At a median follow-up of 30.5 months, median PFS was 13.8 in the durvalumab arm compared to 9.4 months in the placebo arm, with a non-statistically significant trend toward improved PFS with the immunotherapy (HR, 0.85; 95% CI: 0.65–1.12; P=0.247) (Figure). No significant difference in OS was reported with durvalumab compared to placebo (HR, 1.03; 95% CI: 0.78–1.39; P=0.823).
Regarding the safety profile, in the first 4 months of concurrent treatment, a higher number of adverse events (AEs) leading to death or discontinuation occurred in the durvalumab arm. Rates and severity of pneumonitis or radiation pneumonitis were similar between groups, and safety and tolerability were consistent with the known profiles for each treatment.