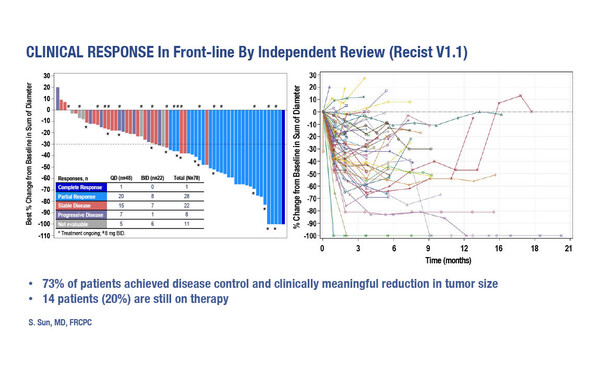
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor shows signs of efficacy in treatment-naïve NSCLC with HER2 exon 20 insertions, but its safety profile remains a limiting factor
In a Mini Oral Session at the ESMO Targeted Anticancer Therapies Congress 2022, results were presented from the ZENITH20-4 trial of poziotinib in treatment-naïve patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and HER2 exon 20 insertions (Abstract 26MO).
Poziotinib, an irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets EGFR and HER2 exon 20 mutations, is being investigated in treatment-naïve or previously treated patients with advanced NSCLC and EGFR or HER2 exon 20 insertions, in different cohorts of the open-label ZENITH20 phase II trial (NCT03318939). Once-daily dosing of poziotinib was originally investigated; however, an exploratory study of twice-daily dosing was added to try to improve tolerability (Ann Oncol. 2021;32 suppl_1:S14–S19). In the presented cohort, 48 treatment-naïve patients with NSCLC and HER2 exon 20 insertions received poziotinib 16 mg once daily, while 22 patients received poziotinib 8 mg twice daily.
Combining results from both doses, the primary endpoint of objective response rate (ORR) was 41% (95% confidence interval 30–54%), with a further four unconfirmed responses. Duration of response was 5.7 months (range 1.2 to >19.1 months), with median progression-free survival (PFS) of 5.6 months (range 0 to >20.2 months). “These efficacy data are interesting and consistent with previous reports, including the ones from the pre-treated setting (J Clin Oncol. 2021;JCO2101323),” says Dr Antonio Passaro from the European Institute of Oncology, IRCCS, Milan, Italy. “However, the here reported response rate in treatment-naïve patients is inferior compared with the one obtained in pre-treated patients who received trastuzumab deruxtecan, where the ORR was 55% and median PFS was 8.2 months. This last is expected to become a landmark for NSCLC harbouring HER2 mutations (N Engl J Med. 2022;386:241–251).”
Regarding tolerability, 90% of patients had dose interruptions and 79% required dose reductions with once-daily poziotinib, while 68% had dose interruptions and 64% had dose reductions with twice-daily poziotinib. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred more frequently with once-daily versus twice-daily poziotinib, namely rash (35% and 18%, respectively), stomatitis/mucosal inflammation (21% and 14%) and diarrhoea (15% and 14%). “The safety profile of poziotinib is characterised by high rates of dose interruptions and dose reductions,” comments Passaro, “And although the tolerability of twice-daily dosing appears more manageable than that of once-daily dosing, toxicity may still be a limiting factor.”
Abstract discussed:
Sun S, et al. Efficacy and safety of poziotinib in treatment-naïve HER2 exon 20 insertion (ex20ins) mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ZENITH20-4. ESMO Targeted Anticancer Therapies Congress 2022, Abstract 26MO
Mini Oral Session, 07.03.2022, h. 17:15 – 18:20, Channel 1