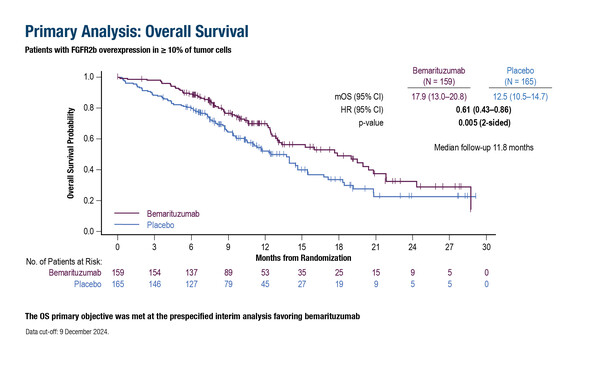
Positive initial overall survival data were, however, attenuated and may not be clinically meaningful in a longer-term analysis
The first-in-class fibroblast growth factor receptor 2b (FGFR2b) inhibitor, bemarituzumab, combined with mFOLFOX6 improved overall survival (OS) versus placebo plus mFOLFOX6 in patients with FGFR2b-overexpressing, unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer (G/GEJC), according to results presented at today’s Presidential Symposium at the ESMO Congress 2025 (Berlin, 17–21 October) (LBA10).
The majority of gastroesophageal cancers are TP53-mutated, chromosomally unstable tumours with co-occurring alterations that make targeting individual oncogenes difficult. Tumour immunohistochemistry – for mismatch repair (MMR), HER2, PD-L1 and CLD18.2 – is used to direct first-line therapy, with variable biomarker overlap. FGFR2b fulfils an important unmet need where there is no actionable target, with approximately 16% of patients having FGFR2b protein overexpression in ≥10% of tumour cells (JCO Precis Oncol. 2025:9:e2400710). The selective inhibitor, bemarituzumab, previously showed promising signs of efficacy in patients with FGFR2b overexpression in the phase II FIGHT trial (Gastric Cancer. 2024;27:558–570), providing the rationale for the phase III FORTITUDE-101 trial.
As presented in Berlin, the primary endpoint was met in a cohort of 324 patients with FGFR2b overexpression in ≥10% of tumour cells: median OS at a pre-specified interim analysis was 17.9 months in the bemarituzumab arm and 12.5 months in the placebo arm (hazard ratio [HR] 0.61; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.43–0.86; p=0.005) at a median follow-up of 11.8 months. Median progression-free survival was 8.6 months with bemarituzumab versus 6.7 months with placebo (HR 0.71; 95% CI 0.53–0.95; p=0.019) at a median follow-up of 11.1 months. The objective response rate (ORR) was 45.9% with bemarituzumab versus 44.8% with placebo (p=0.90).
In a later analysis with a median follow-up time of 19.4 months, the difference in median OS between the treatment arms was minimal (14.5 months versus 13.2 months; HR 0.82; 95% CI 0.62–1.08). Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events were reported in 60% of patients in the bemarituzumab arm, most commonly reversible corneal events, compared with 18% in the placebo arm.
“The initial OS findings demonstrated 5 months’ difference, which is clinically significant and, per the amended study statistics, was declared as the primary analysis, although the median follow-up was less than 1 year and around 40% of patients were enrolled within the last 6 months of the study,” notes Dr Yelena Janjigian from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY, USA. She adds: “Seven months later, with longer follow-up, the converging OS and PFS curves indicate only a weak signal for efficacy. This attenuation likely reflects data maturity and biomarker heterogeneity and not treatment imbalance as treatment exposure and second-line therapy were similar in both groups.”
Preclinical studies indicate that bemarituzumab modulates the tumour microenvironment to sensitise tumours to anti-PD1 antibodies (MAbs. 2021;13:1981202). The ongoing phase Ib/III FORTITUDE-102 trial is exploring mFOLFOX6 plus nivolumab and either bemarituzumab or placebo in patients with FGFR2b overexpression in ≥10% of tumour cells (NCT05111626; J Clin Oncol. 2022;40(Suppl 16):TPS4165). “In FORTITUDE-101, only 37% of patients had PD-L1 combined positive score ≥5% and if this is representative of the FGFR2b-high population, the combined efficacy of nivolumab plus bemarituzumab may be sufficient to improve outcomes in FORTITUDE-102,” notes Janjigian, who concludes: “Despite the encouraging primary OS data in FORTITUDE-101, we need to see additional data to determine if bemarituzumab will become established as a first-line treatment – it is possible that it may have some value in later lines of therapy.” She points to future promising strategies aimed at overcoming heterogeneity and focal positivity including FGFR2b antibody–drug conjugates, biparatopic antibodies promoting receptor degradation, bispecific antibodies (e.g., FGFR2b × CD3 or PD-1) and early PROTAC degraders eliminating FGFR2 signalling.
Programme details:
Rha SY, et al. Bemarituzumab (BEMA) plus chemotherapy for advanced or metastatic FGFR2b-overexpressing gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer (G/GEJC): FORTITUDE-101 phase 3 study results. ESMO Congress 2025 - LBA10