Final overall survival results are now awaited to confirm the place of the combination treatment as a standard approach
The final progression-free survival (PFS) results of the phase III Chinese ASTRUM-007 study presented at ESMO Asia Congress 2022 (Singapore, 2–4 December) confirm that adding immunotherapy to first-line chemotherapy improves outcomes in patients with previously untreated PD-L1-positive oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) (Abstract 69O).
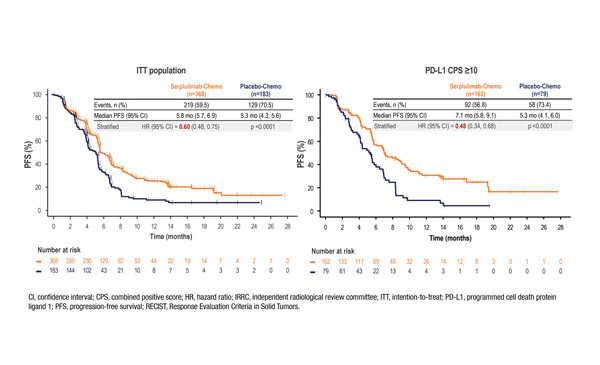
At a median follow-up of 14.9 months, median PFS was 5.8 months (95% confidence interval [CI] 5.7–6.9) with serplulimab plus cisplatin/5-fluorouracil compared with 5.3 months (95% CI 4.3–5.6) with chemotherapy alone (hazard ratio [HR] 0.60; 95% CI 0.48–0.75; p<0.0001) in 551 patients (randomised 2:1). PD-L1 expression was defined as a combined positive score ≥1. Interim overall survival (OS) analysis showed a significant improvement with serplulimab plus chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone (15.3 months [95% CI 14.0–18.6] versus 11.8 months [95% CI 9.7–14.0]; HR 0.68; 95% CI 0.53–0.87; p=0.0020). Grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were reported in 52.6% of patients receiving serplulimab plus chemotherapy and in 48.2% receiving chemotherapy alone. Deaths due to TRAEs occurred in 2.9% and 1.8% of patients receiving serplulimab plus chemotherapy or chemotherapy alone, respectively.
Interim results from the study led to the acceptance by China’s National Medical Products Administration of a New Drug Application for serplulimab plus chemotherapy for locally advanced/recurrent or metastatic ESCC.
“These are relevant and interesting findings for a disease that has a very poor prognosis,” says Dr Valentina Gambardella from INCLIVA-Biomedical Research Institute, HCUV, Valencia, Spain, explaining, “It is only recently that the use of immunotherapy has shown an improvement of clinical outcomes for both adenocarcinoma and squamous cell oesophageal cancer.”
This year has seen the publication of several phase III trials – among them the CheckMate 648 (N Engl J Med. 2022;386:449–462) and ORIENT-15 (BMJ 2022;377:e068714) trials – reporting the benefits of first-line immune checkpoint inhibitor/chemotherapy combinations over chemotherapy alone for PD-L1-positive squamous cell disease. The results of the ASTRUM-007 trial confirm earlier signals of the activity of serplulimab plus chemotherapy in other types of cancer and provide important support for this treatment approach in ESCC.
Gambardella continues, “Although the PFS was significantly improved in the serplulimab-based treatment arm, the OS data are only preliminary and we will need to wait for the final OS results before decisions can be made regarding the place of this treatment as a standard approach.” Looking to the future, Gambardella concludes, “Next steps in this area are to find more sensitive biomarkers than PD-L1 expression to enable better identification of patients with ESCC most likely to respond to immunotherapy-based treatment and to look at alternative, effective combination partners for serplulimab, such as other immune checkpoint inhibitors.”
Abstract presented:
Huang J, et al. First-line serplulimab versus placebo in combination with chemotherapy in PD-L1-positive oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ASTRUM-007): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre phase 3 study. ESMO Asia Congress 2022, Abstract 69O
Proffered Paper Session: Gastrointestinal tumours 02.12.2022, h. 16:15 – 17:45, Hall 406. Also watch the session on the Congress virtual platform