
Trustworthy and explainable AI – a key to equitable oncology?
Mitigating research biases by rigorous data analysis and validation can pave the way for a wider adoption of artificial intelligence in cancer care

Mitigating research biases by rigorous data analysis and validation can pave the way for a wider adoption of artificial intelligence in cancer care

Preclinical findings show antitumour activity of triple KRAS inhibition in mouse models, but it will take years of rigorous research to assess its clinical efficacy in oncology patients

The update reflects survival benefits of post-diagnosis exercise in stage II–III colon cancer as recently reported in the CHALLENGE study

Dose optimisation of immune checkpoint inhibitors may help address current healthcare resource constraints and improve treatment access

Several misconceptions around sex- and gender-sensitive medicine still limit its application in cancer research and care
In a real-world study, multimodal artificial intelligence models outperform PD-L1 across key endpoints

Manageable safety and encouraging antitumour responses were presented with MK-1084 monotherapy and combination regimens

Data shows that index lesion-focused ipsilateral systematic biopsy is not inferior to standard systematic biopsy
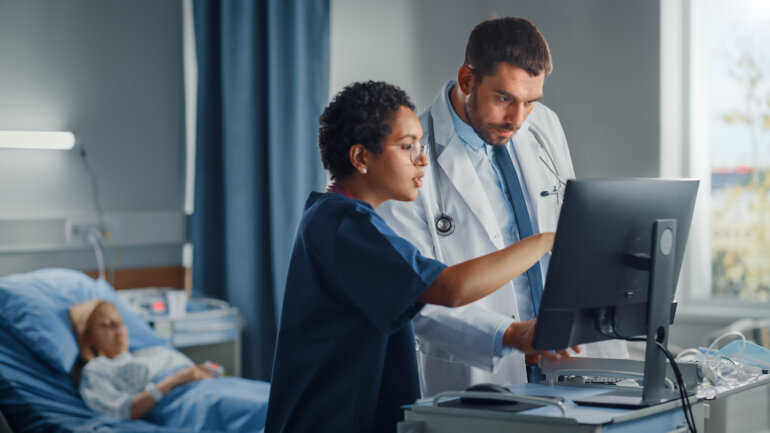

A study compared the performance of different models using routinely collected clinicopathological data from women with HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer

Integrating DNA and RNA profiling is a promising approach to advance cancer characterisation and guide clinical decision-making
This site uses cookies. Some of these cookies are essential, while others help us improve your experience by providing insights into how the site is being used.
For more detailed information on the cookies we use, please check our Privacy Policy.
Necessary cookies enable core functionality. The website cannot function properly without these cookies, and you can only disable them by changing your browser preferences.